SA Article:
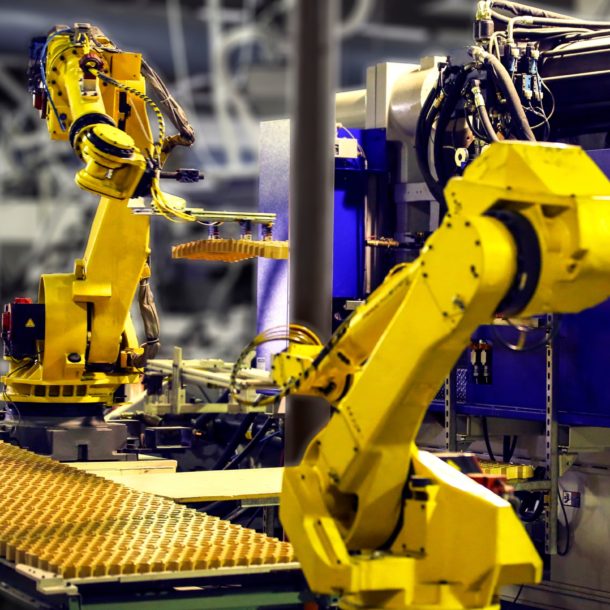
Automation and IR 4.0 in the Manufacturing Industry
Robotics, machine learning, industrial IoT, and other digital technologies are advancing the future of manufacturing automation. Manufacturers are turning to automation and Industry 4.0 technologies to enhance their efficiency as they continue to push for consistency, higher output and lower costs.
In this article, we’ll look at how automation is used in manufacturing, covering the many forms of automation and the main advantages of automation.
Definition of Automation in the Manufacturing Sector

In the context of manufacturing, automation refers to the use of equipment and technology to automate systems or production processes. The fundamental objective is to improve efficiency by expanding production capability or lowering costs, or perhaps both.
Automation has come to be seen as the use of machines to minimise human labour. It has become synonymous with electromechanical systems that may be programmed to execute a variety of jobs and processes. Most manufacturers may certainly benefit from the implementation of automation in their business. Some types of automation in the industry includes: fixed, programmed, or flexible.
Types of Manufacturing Automation
Fixed Automation
Fixed automation, sometimes referred as hard automation, has a predefined task that is difficult to alter or modify from one job to the next. The main programming is located within individual machines. The equipment or production line determines the pace and order of processes. Fixed automation has a high initial cost and therefore it is ideal for mass-production or producing products in high quantities.
Programmable Automation
Programmable automation, often known as soft automation is associated with batch production and has the ability to adjust the order of tasks to adapt with various product design configurations. Programmable automation allows for the production of a wider range of parts and products by preparing new programs or set of instructions for the system.
However, to change the program and tools require downtime which affect the production line and incur costs. This downtime should be considered and factored into batch sizes and total lead times.
Flexible Automation
Due to the downtime, programmable automation has been extended to include flexible automation. Changeovers can be performed automatically with minimal downtime with flexible automation. This may limit the equipment’s ability to run components with identical tools or necessitate the use of additional devices to allow for automated changeovers.
Furthermore, because the programs must be modified, flexible automation is frequently linked to a network, which adds value by allowing remote monitoring and control. Programs can be developed offline and the programmer may integrate them into existing production from anywhere in the world, depending on how the equipment is connected.
Benefits of Automation in Manufacturing
Automation is rapidly being used by manufacturers to improve precision, consistency, and operating efficiency. To begin, objectives and goals must be identified. The clearer the objectives, the more likely they are to be achieved. While generic goals like boosting output are important, automation could also highlight the understanding what affects productivity, which is very important in the manufacturing industry.
Sensors and devices that monitor equipment and create user-friendly data, visuals, and other outputs will aid in connecting production lines and provide additional benefits such as reducing downtime, provide predictable maintenance and improve the decision making process.
Installing devices and equipment to monitor materials in inventory or at a workstation helps cut down on downtime caused by material shortages. Having the ability to identify machinery operational hours may be enough to reduce downtime by optimizing work processes to reduce changeovers, and it may even highlight where additional automation would deliver a good return on investment.

Monitoring could assess the performance of the equipment and notify when it needs maintenance or malfunctions. Performance tracking can aid in making better business decisions and scheduling maintenance at times when it will have the least impact on productivity. Automation and monitoring help businesses make better judgments.
Manufacturers can use real-time data to better understand lead times and deliver more precise estimations and timelines. Automated devices also enhance consistency, which can improve quality by reducing variability in manufacturing. Overall, automated monitoring provides a more predictable model from which to make business decisions, as well as transparency for all stakeholders.
Automation in Salutary Avenue Manufacturing Services
Progressing towards automation proves to be an importance in manufacturing sectors, especially in the air filtration system industry. Salutary Avenue Manufacturing Services are turning to automation and Industry 4.0 technologies to enhance our efficiency as we continue to provide the best quality products and services for our customers.
To make the best of the automation revolution, we have implemented new technologies and equipped our factories with various autonomous machines. Through automation, we continue to aim to be a global company in providing product and services to the power generation industries and a world market leader based in Malaysia for filter products and filtration systems.
Click here to learn more about high performance air filtration systems and our contamination control technologies.
About Author

Muhammad Azim
Azim is a technical associate at Salutary Avenue.
He writes about technology, company updates and business developments.
Share this article